How a Boutique Hair Company Scaled Their E-Commerce Site
In today’s competitive beauty and retail market, customer experience, performance, and scalability are no longer luxuries they are expectations. For one ambitious boutique hair company, the limitations of their WooCommerce-powered site began to restrict growth and efficiency. That’s when they partnered with a professional services team to build a fully customized MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js) e-commerce platform.
This post explores why the shift was necessary, the trade-offs of going custom, and the measurable business outcomes that followed.
Background: A Boutique Hair Business with Big Ambitions
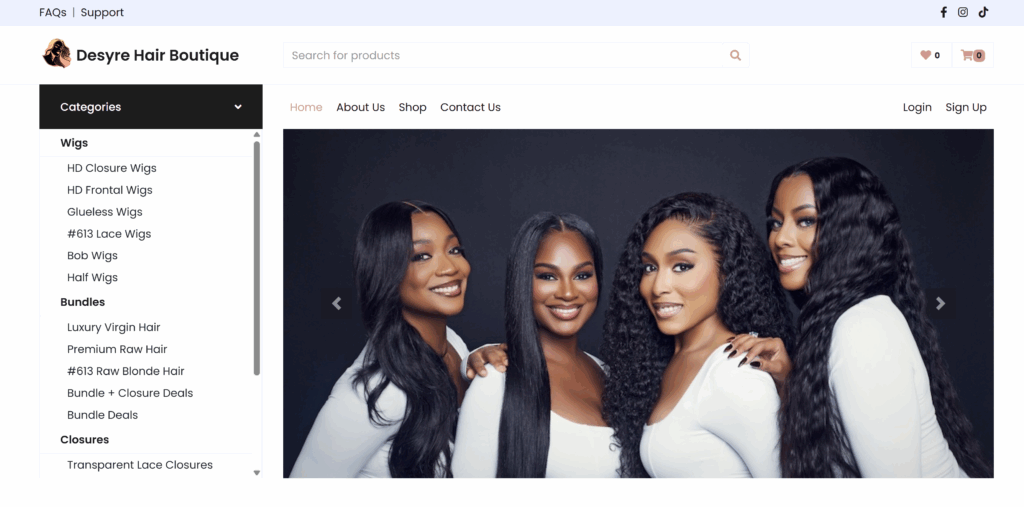
Desyre Hair Boutique specializes in premium wigs, bundles, closures, and frontals. Their goal: to deliver a luxury shopping experience online with the same ease as in-person consultations.
Initially, they launched on WooCommerce for affordability and speed—but as their brand gained traction, cracks began to show.
Pain Points of WooCommerce

While WooCommerce provided a quick entry point into e-commerce, the platform’s limitations became more evident as the business scaled.
1. Performance Bottlenecks
- Slower load times as product images, plugins, and traffic grew
- Frequent downtime during product drops and flash sales
2. Customization Constraints
- Rigid checkout process without support for installment plans or bundle builders
- Limited control over the front-end experience without heavy plugin reliance
3. Security & Maintenance
- Dependence on third-party plugins created security vulnerabilities
- WordPress updates often broke site elements or customizations
Why a Custom MERN Stack Solution?
To overcome these barriers, DHB engaged MIS professional services team to design and develop a custom MERN stack platform tailored to their specific needs. The new system offered complete control, performance optimization, and scalable architecture.
WooCommerce vs. Custom MERN Stack: Pros & Cons
| Feature | WooCommerce | Custom MERN Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited by hosting & plugins | Optimized with server-side rendering & APIs |
| Customization | Dependent on plugins | Full flexibility across UI & workflows |
| Security | Plugin vulnerabilities | Custom security protocols |
| Scalability | Works for small-to-mid catalogs | Built for growth & enterprise-level |
| Time to Launch | Quick setup | Longer dev lifecycle |
| Maintenance | Requires plugin monitoring | Needs dev support, but fewer risks |
| Cost | Low upfront, higher plugin costs | Higher upfront, lower long-term costs |
Features of the New Custom Platform

- Dynamic product filters (by texture, length, color, type)
- AI-powered wig size recommender
- Custom bundle builder (mix-and-match closures, wefts, lace)
- Integrated payment options (Klarna, AfterPay)
- Real-time inventory management
- Customer dashboard with loyalty points & order tracking
- Mobile-first design optimized for 90%+ mobile shoppers
Quantified Success
Business Outcomes:
- +60% Conversion Rate in first 3 months
- 2x Increase in Average Order Value through upselling & bundling
- 50% Reduction in Cart Abandonment
- 75% Drop in Support Tickets related to order tracking
Customer Outcomes:
- Faster load times: from 7 seconds → 1.2 seconds
- Improved mobile experience: +40% engagement
- Flexible payments: Klarna & AfterPay cited as key decision factors
Voices from the Journey
Business Owner:
“Our old WooCommerce site was holding us back. With the custom app, we’re finally in control and able to scale confidently.”
Customer:
“I never thought I’d buy a wig online, but the sizing tool and bundle builder made it easy and splitting payments sealed the deal.”
Final Thoughts: Should You Go Custom?
For DHB, outgrowing WooCommerce was inevitable. While custom MERN development requires more upfront investment, the long-term gains—in scalability, customer experience, and reduced operational friction—delivered a strong ROI.
A custom platform isn’t for every business, but for brands whose growth is outpacing WooCommerce’s capabilities, a tailored solution built by a professional services team may be the key to unlocking the next level of success.
Ready to Scale Beyond WooCommerce?
If your business is hitting similar roadblocks, consider whether a custom tech build is right for your growth strategy. The right platform could be the difference between keeping up and breaking through.




